Current Divider Rule (CDR) is only valid for a parallel circuit as shown in figure below. CDR is used to calculate the current at one of the resistors. By using CDR, summation of all voltages from each resistor will equal to the current source as what has been stated by Kirchhoff Current Law (KCL). The current division starts from the main source and continue till end of the circuit.
CDR:
I1 = [R2/(R1 + R2)] * IT;
I2 = [R1/(R1 + R2)] * IT;
KCL:
IT = I1 + I2
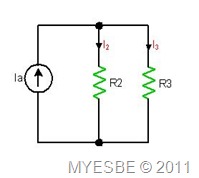
Example 1
Find I3.
STEP 1:
Start from the source, and convert the circuit such that it only has two resistors connected in parallel.
STEP 2:
Use CDR to calculate Ia.
Ia = [R1/(R1 + Ra)]*IT
STEP 3:
I3 = [R2/(R2 + R3)]*Ia
Example 2
Find I3.
STEP 1:
Start from the source. Because it is a voltage source, then we need to find its total current. Total current can be calculated by using total voltage divide the total resistance.
IT = V/(R1//R2//R3)
Once IT is calculated, next step is the step that is similar to as example 1.
NB: Noted that I3 is actually can be calculated without using CDR. Ohm’s law is just enough to solve the circuit above. I3 = V/R3.





















0 comments:
Post a Comment