1. The symbol is C and the unit is Farad.
2. “Watt” is the unit for Power.
3. Charge is an electrical property of the atomic particles of which matter consists, which is measured in coulombs (C).
4. Ohm is the unit for resistance.
6. It contains 6.24 x 10^18 electrons in one coulombs.
7. Electric current is the time rate of charge, which is measured in amperes (A).
8. Direct current is a current that remains constant with time and alternating current is a current that is varies with time. In details, direct current is always 5V (for example) at one second, two seconds or even twenty seconds. Alternating current however is the current that is 2V (for example) at one second, 5V (for example) at two seconds and perhaps 0V (for example) at fifteen seconds.
9. 1A = 1C/s => 2A = 2C/s
1 coulomb contains 6.24 x 10^18 electrons
Therefore, 2C/s = 2 x (6.24 x 10^18) /s = (12.48 x 10^18)/s
In 30 seconds = [(12.48 x 10^18)/s ] x 30s = 374.4 x 10^18 electrons.
10. Voltage (or potential difference) is the energy required to move a unit charge through an element, measured in volts (V). “Volt” is the unit for voltage.
11. Power is the time rate of expending or absorbing energy, measured in watts (W). “P” is the symbol for power.
12. Active elements and Passive elements.
13. An active element is an element that is capable of generating energy while a passive element is an element that is not capable of generating energy. Example of passive elements are resistor, inductor and capacitor whereas for active elements are sources.
14. Example of passive elements are resistor, inductor and capacitor
15. Sources can be divided into two types that are independent and dependant sources. An independent source is an active element that provides a specified voltage or current that is completely independent of other circuit elements. A dependent source however is an active element in which the source quantity is controlled by another parameter (voltage or current).
16. Energy is the capacity to do work. The reason of calculating energy in electrical based system is to determine the total energy delivered/consumed by the system in a certain period of time.
17.
18.
200W x 8 =1600Wh
3 x 60W x 12 = 2160Wh
Total energy used = 1600Wh + 2160Wh = 3.76kWh
Bill per day = 3.76kWh x RM 0.30 = RM 1.128
Bill for a year = RM 1.128 x 365 = RM 411.72
19. W = QV = (20)(0.5) =10J
20.
| Independent | Dependent |
| provides a specified voltage or current that is completely independent of other circuit elements | A dependent source is an active element in which the source quantity is controlled by another voltage or current |
| Symbol => round shape | Symbol => diamond shape |
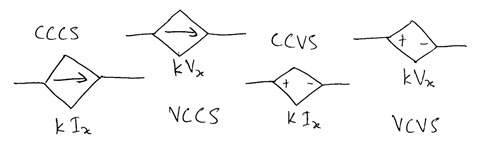
21.
CCCS –> Current Controlled Current Source
VCCS –> Voltage Controlled Current Source
CCVS –> Current Controlled Voltage Source
VCVS –> Voltage Controlled Voltage Source
22.
Energy per day = 800W x (5/60) = 66.67Wh
Energy per month = 66.67Wh x 30 = 2000Wh
Total cost = 2kWh x RM 0.27 = RM 0.54
23. FALSE
24.
5 x 75W x 4 = 1500Wh
1.5kW x (30/60) = 750Wh
Daily cost => 2.25kWh x RM 0.30 = RM 0.675
One week => RM 0.675 x 7 = RM 4.73
25. A circuit element has current, i(t) = 10e^-0.5t A and voltage, v(t) = 10 di/dt V. Calculate the power of the elements and the energy in 5 seconds.
v(t) = 10 di/dt
= 10 d(10e^-0.5t)/dt
= 10 (-0.5)(10e^-0.5t)
v(t) = –50e^-0.5t
i(t) = 10e^-0.5t
P = iv
= (10e^-0.5t)(–50e^-0.5t)
= -500e^(0.5t-0.5t)
= –500e^-t W
26.
6 x 100W x 10 = 6kWh
Daily cost => 6kWh x RM 0.30 = RM 1.80
Weekly cost => RM 1.80 x 7 = RM 12.60




















0 comments:
Post a Comment